

When the goods are shipped long distances, say from Hong Kong to the United States, it is usually impractical and too expensive for the seller to pay for return transportation.The buyer can refuse to honor payment on any grounds.However, in practice, there are risks involved: On the surface, D/P transactions seem fairly safe from the seller’s perspective. If the buyer fails or refuses to pay, the exporter has the right to recover the goods and resell them. The buyer has to settle the payment with the bank before the documents are released and he can take delivery of the goods. The D/P transaction utilizes a sight draft, where payment is on demand.Īfter the goods are shipped, the exporter sends the sight draft to the clearing bank, along with documents necessary for the importer/buyer to obtain the goods from customs.
#LETTER OF CREDIT DRAFT ACCOUNTEE FULL#
Payee: The party to whom the bill is payable usually the seller’s bank.īills of exchange are either payable at sight ( sight drafts) where the bank pays the full amount upon presentation, or payable at some future date ( time or term drafts).Drawee: The recipient of the bill of exchange for payment or acceptance usually the buyer.Drawer: The party issuing the bill of exchange usually the exporter/seller.It is generally a three-party instrument consisting of a: Although written by the seller, it has the equivalent effect of a check written by the buyer. Both rely on an instrument widely used in international trade called a bill of exchange or draft.Ī bill of exchange, or draft, is a negotiable instrument that is both drawn up by and made payable to the exporter/seller.
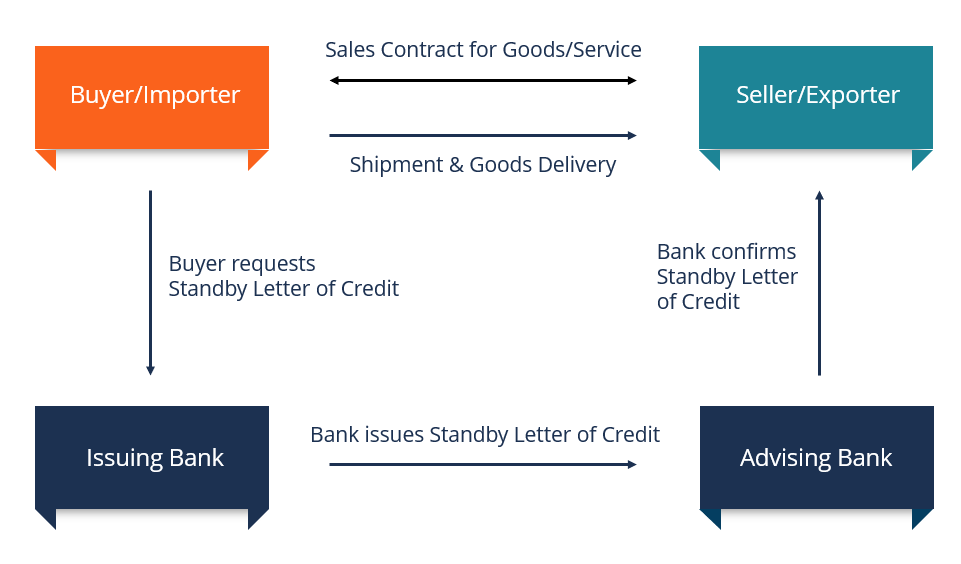
These represent risk levels lower than an O/A, but greater than an L/C.

In the international arena, open account sales are regarded as having the most risk letter of credit transactions as having the least.īetween these two poles, however, are two lesser-known transaction types: Documents Against Payment (D/P) and Documents Against Acceptance (D/A). Most sellers are very familiar with Open Account (O/A) and Letter of Credit (L/C) transactions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
